Geography
![Source: By Croquant (Own work) [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](http://chinaenv.colgate.edu/waterpollution/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/11/Location_of_Kunming_City_Districts_within_Yunnan_China.png)
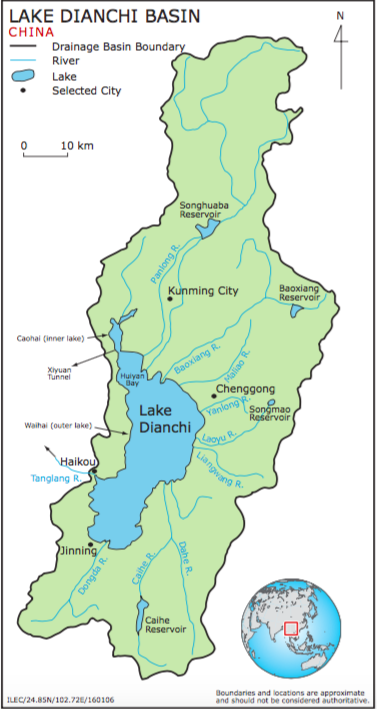
Caohai experiences much more concentrated pollution that Waihai. Some studies have decided it is more suitable to treat the two sections of the lake as separate lakes because their pollution levels differ so extremely (Li, Dong, Zhao, Zhang, Cui, and He, 2007, p. 292). Several rivers run into the Waihai section, but before reaching Lake Dianchi these rivers run through polluted cities and villages in Yunnan Province and carry this pollution with them to the lake (Liu et al, 2015, p. 3768).
The Pollution
Yunnan Province has long been primarily agricultural, but the Dianchi basin has witnessed high industrial growth and boasts the highest population density within Kunming City (Liu et al, 2015, p. 3768).
In the late 1990’s to early 2000’s, Lake Dianchi was identified as one of the 3 top water pollution concerns in the country (Zhang et al, 2014, p. 1498). In 2009, the pollution reached its peak when the lake was classified worse than a Stage 5 (too dangerous for human contact)—the lowest rank on the scale used by China (Liping et al, 2006, p. 3772).
![Pollution in Lake Dianchi Source: By shizhao (http://www.flickr.com/photos/shizhao/9633004367/) [CC BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](http://chinaenv.colgate.edu/waterpollution/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/11/1024px-滇池2013.jpg)
Sources of pollution:
Pollution is brought to the lake from its inflowing rivers that have been contaminated due to the expansion of industrial practices and heavy migration patterns. “Factors such as fragile ecological conditions, a shallow water level, insufficient inflow, and the age stage of the lake have caused the pollution in the lake to be more serious and the water quality to become increasingly deteriorated” (Zhang et al, 2014, p. 1497).
![Industry in Kunming Source: By Philippe Semanaz from Paris, France (Industry) [CC BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](http://chinaenv.colgate.edu/waterpollution/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/11/Kunming_Industry.jpg)
Source: Semanaz, P. (2005).
Changes in land use
During Mao’s time, the demands for development, industrialization, and progress led to the practice of land reclamation. Land reclamation required intense topographical and hydrological alterations to land masses, which increased pollution by encouraging erosion, threatening biodiversity, and closing the gap between human practices and natural ecosystems.
Lake Dianchi’s watershed has undergone massive land use changes in recent decades. From 1974 through 2008, urban industry expanded into agricultural land, and agriculture was forced to expand into the North and South of the watershed (Zhang et al, 2014, p. 3857). Pollutants from agriculture, such as fertilizers and livestock waste, have increased as has industrial pollution, enhanced by a lack of waste management programs and weak enforcement of environmental protection practices.
Where Lake Dianchi Stands Now
The increasing industrialization along with the increasing movement of people (migration) and a growing population have led to a growing demand for water resources (Zhou et al, 2012, p. 3853). Since 2009, the peak of the pollution, there has been a gradual increase in water quality due to a significant amount of capital invested in pollution control of the Lake Dianchi basin.
Works Cited
Croquant (Own work). (2007). Location of Kunming prefecture (yellow) within Yunnan province of China [digital image]. Retrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Location_of_Kunming_Prefecture_within_Yunnan_(China).png
Figure 1 from Liping, H., Li, W., & Xiangcan J. (2006). Lake Dianchi: Experience and Lessons Learned Brief. ( No. 11). Geneva: Lake Basin Management Initiative.
Semanaz, P. (2005). Kunming industry [digital image]. Retrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kunming_Industry.jpg
Shizhao (Photographer). (2013). [digital image]. Retrieved from https://www.flickr.com/photos/shizhao/9633004367/
Li, R., Dong, M., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Cui, Q., & He, W. (2007). Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of plateau lakes in yunnan (china). Journal of Environmental Quality, 36(1), 291.
Liping, H., Li, W., & Xiangcan, J. (2006). Lake Dianchi: Experience and Lessons Learned Brief. ( No. 11). Geneva: Lake Basin Management Initiative.
Liu, W., Wang, S., Zhang, L., & Ni, Z. (2015). Water Pollution Characteristics of Dianchi Lake and the Course of Protection and Pollution Management. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(5), 3767-3780. DOI:10.1007/s12665-015-4152-x.
Zhang, T., Zheng, W. H., Wang, S. R., & Ni, Z. K. (2014). Temporal and Spatial Changes of Water Quality and Management Strategies of Dianchi Lake in Southwest China. EGU: Hydrology and Earth Systems Sciences, 18(4), 1493-1502. DOI:10.5194/hess-18-1493-2014
